How food irradiation works
Food irradiation (the application of ionizing radiation to food) is a technology that improves the safety and extends the shelf life of foods by reducing or eliminating microorganisms and insects. Like pasteurizing milk and canning fruits and vegetables, irradiation can make food safer for the consumer.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for regulating the sources of radiation that are used to irradiate food. The FDA approves a source of radiation for use on foods only after it has determined that irradiating the food is safe. Food irradiation has been evaluated for safety for over 30 years. Agencies and organizations that have endorsed its safety and effectiveness include:
• Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
• United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
• World Health Organization (WHO).
• International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
• National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). When NASA astronauts fly in space, they eat meat that has been sterilized by irradiation to avoid becoming sick with foodborne illnesses.
Irradiation does not make foods radioactive, compromise nutritional quality, or noticeably change the taste, texture, or appearance of food. In fact, any changes made by irradiation are so minimal that it is not easy to tell if a food has been irradiated.
Why Irradiate Food?
Irradiation can serve many purposes, such as:
• Prevention of Foodborne Illness – to effectively eliminate organisms that cause foodborne illness, such as Salmonella and Escherichia coli (E. coli).
• Preservation – to destroy or inactivate organisms that cause spoilage and decomposition and extend the shelf life of foods.
• Control of Insects – to destroy insects in or on tropical fruits imported into the United States. Irradiation also decreases the need for other pest-control practices that may harm the fruit.
• Delay of Sprouting and Ripening – to inhibit sprouting (in potatoes, for example) and delay ripening of fruit to increase longevity.
• Sterilization – irradiation can be used to sterilize foods, some of which can then be stored for years without refrigeration. Sterilized foods are useful in hospitals for patients with severely impaired immune systems, such as patients with AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy. Foods that are sterilized by irradiation are exposed to substantially higher levels of treatment than those approved for general use.
How Food is Irradiated
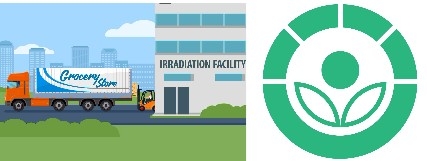
Foods leave processing facilities and arrive at facilities that use radiation to kill germs that can make you sick.
At the irradiation facility, foods ride on a conveyor belt through an irradiation chamber. In the chamber, foods pass under a beam of radiation. This kills germs by breaking the bonds that hold the germ’s DNA together. Once the food leaves the irradiation chamber, most of the germs are destroyed.
The irradiated food goes to grocery stores and food service facilities.
Three sources of radiation are approved for use on foods:
• Gamma rays are emitted from radioactive forms of the element cobalt (Cobalt 60) or of the element cesium (Cesium 137). Gamma radiation is used routinely to sterilize medical, dental, and household products and is also used for the radiation treatment of cancer.
• X-rays are produced by reflecting a high-energy stream of electrons off a target substance (usually one of the heavy metals) into food. X-rays are also widely used in medicine and industry to produce images of internal structures.
• Electron beam (or e-beam) is similar to X-rays and is a stream of high-energy electrons propelled from an electron accelerator into food.
Is Irradiated Food Safe to Eat?
The FDA has evaluated the safety of irradiated food for more than 30 years and has found the process to be safe. The World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) have also endorsed the safety of irradiated food.
The FDA has approved a variety of foods for irradiation in the United States including:
• Beef and Pork.
• Crustaceans (such as lobster, shrimp, and crab).
• Fresh Fruits and Vegetables.
• Lettuce and Spinach.
• Poultry.
• Seeds for Sprouting (such as alfalfa sprouts).
• Eggs in Shells.
• Shellfish and Molluscan or Mollusks (such as oysters, clams, mussels, and scallops).
• Spices and Seasonings.
How to Know if Food Has Been Irradiated?
The FDA requires that irradiated foods bear the international symbol for irradiation. Look for the Radura symbol (pictured, above right) along with the statement “Treated with radiation” or “Treated by irradiation” on the food label. Bulk foods, such as fruits and vegetables, are required to be individually labeled or to have a label next to the sale container. The FDA does not require that individual ingredients in multi-ingredient foods (such as spices) be labeled. It is important to remember that irradiation is not a replacement for proper food handling practices by producers, processors, and consumers. Irradiated foods need to be stored, handled, and cooked in the same way as non-irradiated foods, because they could still become contaminated with disease-causing organisms after irradiation if the rules of basic food safety are not followed.