Skin infections
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
What are skin infections?
Skin infections occur when bacteria infect the skin and sometimes the deep tissue beneath the skin.
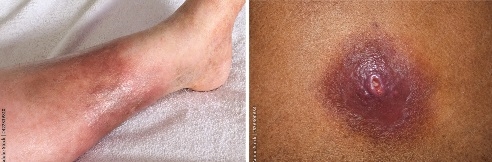
Cellulitis is a common type of skin infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the infected area of the skin (see photo on left of mild cellulitis to a lower leg).
Another type of skin infection is skin abscess, which is a collection of pus under the skin (see photo on right of a skin abcess to a woman's back).
Causes
Normally, different types of bacteria live on a person’s skin. Cellulitis or an abscess can occur if there is a cut or a break in the skin that allows bacteria to enter and cause an infection.
Risk Factors
Some factors can increase the risk of cellulitis, including:
• Injury to the skin.
• Skin conditions, such as athlete’s foot or eczema.
• Chronic swelling of the legs or arms.
• Obesity.
• Diabetes.
Symptoms
Symptoms of cellulitis can come on gradually or suddenly, and include:
• Skin redness.
• Pain, tenderness, or warmth when the affected skin is touched.
• Swelling of the affected area.
An abscess has similar symptoms as cellulitis but also has a collection of pus inside, which can sometimes drain out.
When to Seek Medical Care
• See a doctor right away if your child is younger than 3 months old and has a fever of 100.4 °F (38 °C) or higher.
• See a doctor if you have symptoms of cellulitis or abscess. Although most cases of cellulitis resolve quickly with treatment, some can spread to the lymph nodes and bloodstream and can become life-threatening.
Treatment
Your doctor will determine if you have a skin infection by asking about symptoms and doing a physical examination.
Antibiotics are needed to treat cellulitis.
If you have a skin abscess, your doctor may need to drain the pus from the abscess. Antibiotics are sometimes needed for abscesses after the pus has been drained.
Any time you take antibiotics, they can cause side effects. Side effects can range from minor issues, like a rash, to very serious health problems, such as antibiotic-resistant infections and C. diff infection, which causes diarrhea that can lead to severe colon damage and death. Call your doctor if you develop any side effects while taking your antibiotic.
In some cases, severe infections need to be treated in the hospital.
How to Feel Better
If you are prescribed antibiotics for your skin infection:
• Take them exactly as your doctor tells you.
• Do not share your antibiotics with others.
• Do not save them for later. Talk to your pharmacist about safely discarding leftover medicines.
• Talk with your doctor if you have any questions about your antibiotics.
• Keeping the area clean is important so your skin infection can get better.
• If the infection is in the leg, elevating the leg can help decrease swelling.
Prevention
You can help prevent skin infections by doing the following:
• Clean your hands.
• Wash cuts with soap and water.
• Talk to your doctor about steps you can take to prevent skin infections, especially if you have a condition, such as diabetes, that increases your risk of certain skin infections.