Dengue fever: how you get it, symptoms and treatment
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Dengue or dengue fever is a mosquito-borne illness that occurs in tropical and subtropical areas. Mild dengue fever causes a high fever and flu-like symptoms, while its severe form, often called dengue hemorrhagic fever, can cause serious bleeding, shock and death. Learn more about dengue here: cdc.gov/dengue/index.html.
Dengue fever is most common in Southeast Asia, the western Pacific islands, Latin America and Africa, but has beem known to spread to new areas, such as Europe and the southern United States, although the U.S. outbreaks have been small and limited. Learn about the areas most at risk here: cdc.gov/dengue/areaswithrisk/index.html.
To prevent infection, avoid being bitten by mosquitoes, and take steps to reduce the mosquito population. Learn more about mosquito control here: cdc.gov/dengue/mosquito-control/index.html.
Key Facts
• About one in four people infected with dengue will get sick.
• For people who get sick with dengue, symptoms can be mild or severe.
• Severe dengue can be life-threatening within a few hours and often requires care at a hospital.
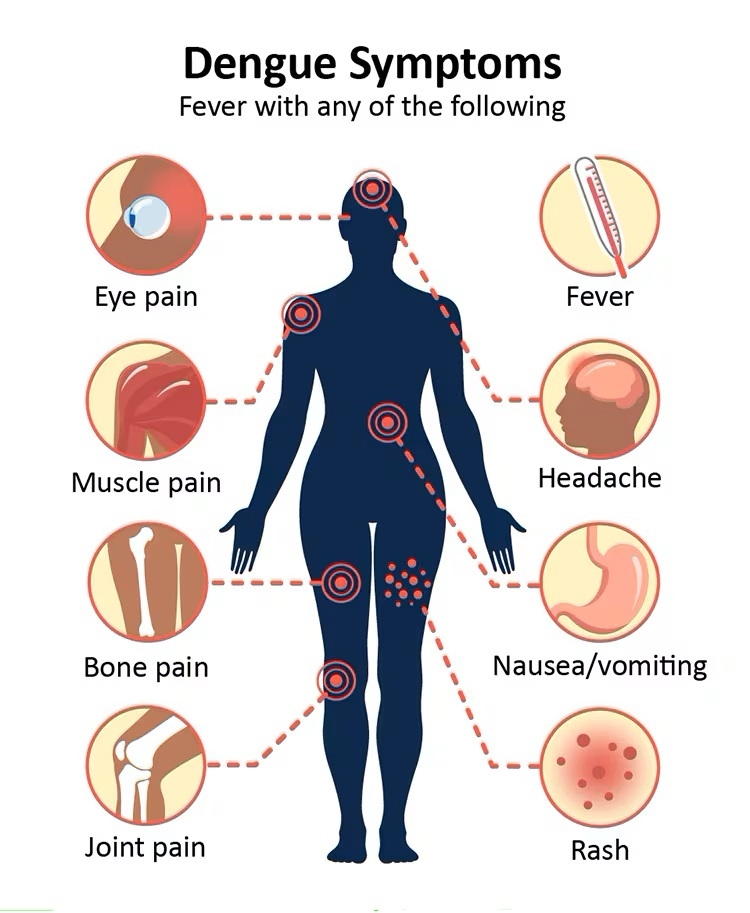
Symptoms
Mild symptoms of dengue can be confused with other illnesses that cause fever, aches and pains, or a rash.
The most common symptom of dengue is fever, with any of the following:
• Nausea, vomiting
• Rash
• Aches and pains. Eye pain, typically behind the eyes; muscle, joint, or bone pain
• Any warning sign
• Symptoms of dengue typically last 2–7 days. Most people will recover after about a week.
Treatment
• There is no specific medicine to treat dengue.
• Treat the symptoms of dengue and see your healthcare provider.
• See a healthcare provider if you develop a fever or have symptoms of dengue. Tell him or her about your travel.
• Rest as much as possible.
• Take acetaminophen (knwn as paracetamol outside of the United States) to control fever and relieve pain.
• Do not take aspirin or ibuprofen!
• Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated. Drink water or drinks with added electrolytes.
• For mild symptoms, care for a sick infant, child, or family member at home.
• Symptoms of dengue can become severe within a few hours. Severe dengue is a medical emergency.
Severe dengue
• About 1 in 20 people who get sick with dengue will develop severe dengue.
• Severe dengue can result in shock, internal bleeding, and even death.
• If you have had dengue in the past, you are more likely to develop severe dengue.
• Infants and pregnant women are at higher risk for developing severe dengue.
Symptoms and warning signs of severe dengue
Watch for signs and symptoms of severe dengue. Warning signs usually begin in the 24 to 48 hours after your fever has gone away.
Immediately go to a local clinic or emergency room if you or a family member has any of the following symptoms:
• Belly pain or tenderness
• Vomiting (at least 3 times in 24 hours)
• Bleeding from the nose or gums
• Vomiting blood, or blood in the stool
• Feeling tired, restless, or irritable
Treatment of severe dengue
• If you have any warning signs, see a healthcare provider or go to the emergency room immediately.
• Severe dengue is a medical emergency. It requires immediate medical care at a clinic or hospital.
• If you are traveling, find health care abroad.